Factoring Calculator
Factor Polynomials & Numbers Instantly
Get complete solutions for trinomials, quadratics, prime factorization, and more. Free, fast, accurate.
Our Factoring Calculator provides fast and accurate solutions for factoring numbers and polynomials. It supports prime factorization, trinomials, difference of squares, difference of cubes, perfect square trinomials, quartic expressions, and GCF with clear step by step explanations. Students use it to check homework, and professionals rely on it for quick, reliable results on any device.
What is Factoring?
Factoring breaks numbers or expressions into smaller pieces that multiply together to give you the original. You can think of it as reverse multiplication.
Here’s a simple example with numbers. When you multiply 3 × 4, you get 12. When you factor 12, you break it back down into 3 and 4.
Number Example:
Number: 12
All factors: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Prime factorization: 2² × 3
The same idea works with algebra. You can break expressions into factors that multiply back to the original.
Polynomial Example:
Expression: x² + 5x + 6
Factored form: (x + 2)(x + 3)
Check by multiplying: (x + 2)(x + 3) = x² + 3x + 2x + 6 = x² + 5x + 6 ✓
Our calculator handles both types. Enter any whole number or algebraic expression, and you get the factors immediately.
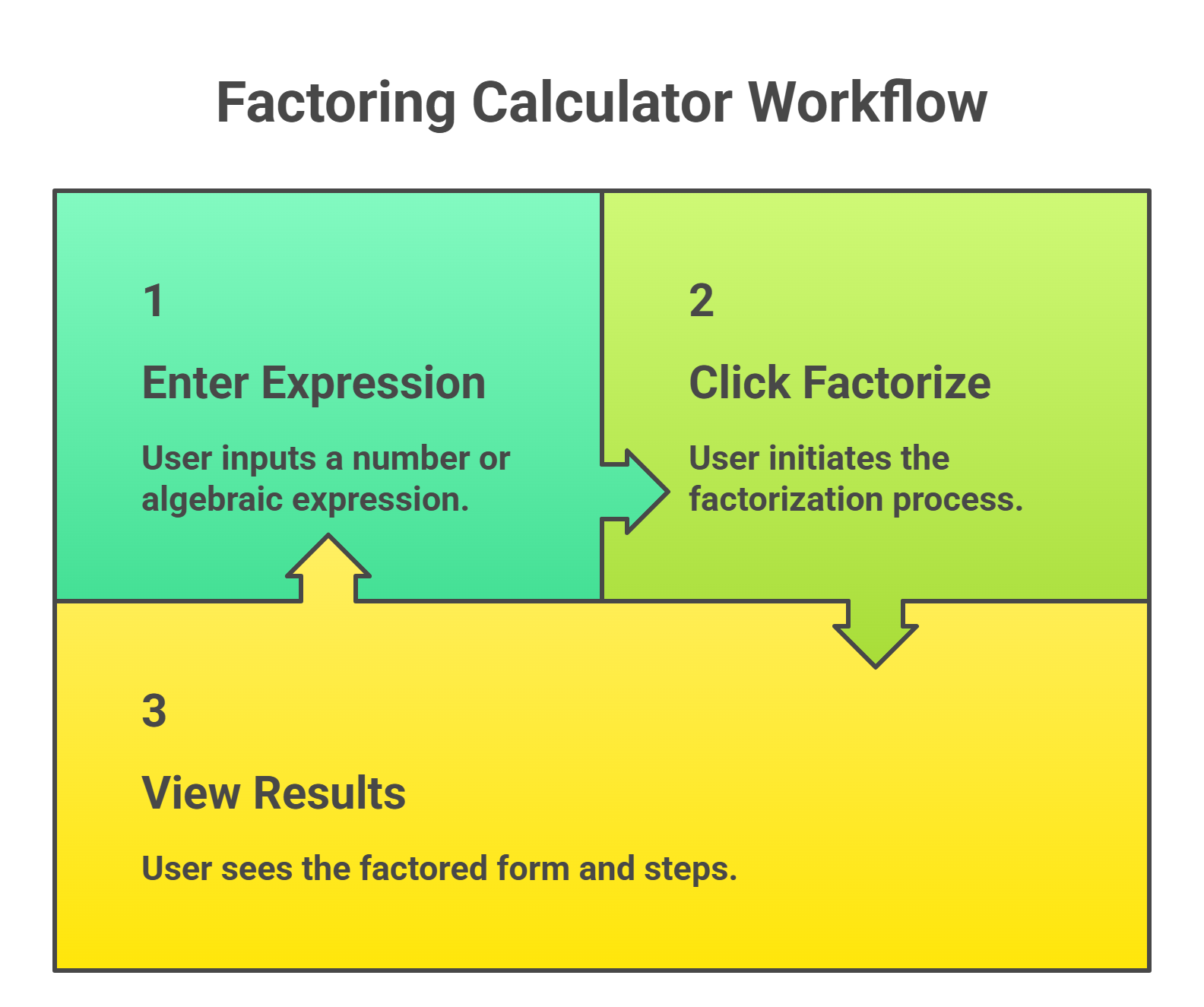
How to Use This Factoring Calculator
The calculator works in three simple steps. No math degree required.
Step 1: Enter Your Expression
Type any of these into the input box:
Whole numbers like 60, 360, or 1024
Simple expressions like x² + 5x + 6
Complex polynomials like 6x² + 7x – 5
Special patterns like x² – 49 or x³ – 27
Tip: Use the ^ symbol for exponents. Type x^2 instead of x².
Step 2: Click “Factorize Now”
The calculator takes over from here. It detects what type of expression you entered, picks the right method, and solves it in under one second. You see every step in the solution.
Step 3: View Your Results
You get four things with every answer:
Your final factored answer
Complete working that shows each step
The method we used to solve it
A verification check that proves the answer
Not sure what to enter? Click any of the quick example buttons above the calculator. They load different problem types so you can see how each one works.
Why Use a Factoring Calculator?
All Factorization Types We Support
Prime Factorization (Numbers)
What it does:
Breaks whole numbers into their prime factors.
Example:
60 = 2² × 3 × 5
When to use it:
Any whole number you need to factor.
Try 60 now
Trinomial (a = 1) Factorization
What it does:
Factors expressions that match the x² + bx + c pattern.
Example:
x² + 5x + 6 = (x + 2)(x + 3)
When to use it:
Three terms where x² has no number in front.
Try this example
Quartic Form
What it does:
Factors polynomials with x⁴ (fourth degree).
Example:
x⁴ – 81
= (x² – 9)(x² + 9)
= (x – 3)(x + 3)(x² + 9)
When to use it:
Expressions with x to the fourth power.
Try this example
General Trinomial (a ≠ 1) Factorization
What it does:
Factors ax² + bx + c when a is not 1.
Example:
6x² + 7x – 5
= (3x + 5)(2x – 1)
When to use it:
Three terms with a coefficient before x².
Try this example
Difference of Squares
What it does:
Uses the formula
a² – b² = (a – b)(a + b).
Example:
x² – 49 = (x – 7)(x + 7)
When to use it:
Two perfect squares with subtraction between them.
Try this example
Difference of Cubes
What it does:
Applies the a³ – b³ formula.
Example:
x³ – 27 = (x – 3)(x² + 3x + 9)
When to use it:
Two perfect cubes with subtraction between them.
Try this example
Sum of Cubes
What it does:
Applies the a³ + b³ formula.
Example:
x³ + 64 = (x + 4)(x² – 4x + 16)
When to use it:
Two perfect cubes with addition between them.
Try this example
Perfect Square Trinomials
What it does:
Recognizes and factors (a ± b)² patterns.
Example:
4x² – 12x + 9 = (2x – 3)²
When to use it:
Three terms that form a perfect square.
Try this example
Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
What it does:
Pulls out the largest factor shared by all terms.
Example:
2x² + 4x = 2x(x + 2)
When to use it:
Check for GCF first with EVERY expression!
Try this example
Not sure which method to use?
Whole number | Prime factorization |
|---|---|
Two terms | Check for squares or cubes |
Three terms | Look for trinomial patterns |
When to Use Which Factoring Method
Confused about which technique to apply? Follow this simple decision tree:
Is it a whole number?
→ Use Prime Factorization
How many terms does it have?
One term? → Check for GCF only
Two terms? → Try these in order:
- GCF first
- Difference of Squares (both perfect squares, subtraction)
- Sum/Difference of Cubes (both perfect cubes)
Three terms? → Check these patterns:
- GCF first (always!)
- Perfect Square Trinomial?
- Is the x² coefficient = 1? → Trinomial (a = 1)
- Is the x² coefficient ≠ 1? → General Trinomial (AC method)
Four or more terms? → Try Grouping Method
Pro Tip: Always Start with GCF
Before applying any fancy method, check if all terms share a common factor. Pull it out first, then work with what’s left!
Example: 2x² + 10x + 12
Wrong approach: Try to factor as trinomial directly
Right approach:
- First: Factor out GCF of 2 → 2(x² + 5x + 6)
- Then: Factor inside → 2(x + 2)(x + 3)
Worked Examples with Full Steps
Here are three examples that show exactly how the calculator solves different types of problems.
Example 1: Simple Trinomial
Problem: x² + 5x + 6
Method: Trinomial factoring (a = 1)
Step 1: Identify b = 5 and c = 6
Step 2: Find two numbers that multiply to 6 and add to 5
- Try 1 and 6: 1 × 6 = 6, but 1 + 6 = 7 ✗
- Try 2 and 3: 2 × 3 = 6, and 2 + 3 = 5 ✓
Answer: (x + 2)(x + 3)
Check: (x + 2)(x + 3) = x² + 3x + 2x + 6 = x² + 5x + 6 ✓
Example 2: AC Method
Problem: 6x² + 7x – 5
Method: General trinomial (AC method)
Step 1: Identify a = 6, b = 7, c = -5
Step 2: Multiply a × c = 6 × (-5) = -30
Step 3: Find two numbers that multiply to -30 and add to 7
- We need -3 and 10 because (-3) + 10 = 7 ✓
Step 4: Rewrite the middle term: 6x² – 3x + 10x – 5
Step 5: Group the terms: (6x² – 3x) + (10x – 5)
Step 6: Factor each group: 3x(2x – 1) + 5(2x – 1)
Answer: (3x + 5)(2x – 1)
Example 3: Difference of Squares
Problem: x² – 49
Method: Difference of squares
Step 1: Check if both terms are perfect squares
- x² is the square of x ✓
- 49 is the square of 7 ✓
Step 2: Apply the formula a² – b² = (a – b)(a + b)
Answer: (x – 7)(x + 7)
How to Choose the Right Factoring Method
Follow this guide when you have an expression but you’re not sure which method to use.
Start here: Is it a whole number?
YES → Use prime factorization
NO → Go to next question
How many terms does it have?
One term:
Factor out the GCF only
Two terms:
- Both perfect squares? → Difference of squares
- Both perfect cubes? → Sum or difference of cubes
Three terms:
- Always check for GCF first!
- Is the coefficient of x² equal to 1? → Simple trinomial
- Is the coefficient of x² NOT equal to 1? → AC method
- Does it match a perfect square pattern? → Perfect square trinomial
Four or more terms:
Try the grouping method
Critical Rule: Always check for GCF before trying any other method!
❌ Wrong approach:
You have 2x² + 10x + 12
You try to factor x² + 5x + 6 directly
✓ Right approach:
You have 2x² + 10x + 12
Pull out 2 first: 2(x² + 5x + 6)
Then factor inside: 2(x + 2)(x + 3)
Why Factoring Matters
Factoring is not just classroom math. It powers real technology you use every single day.
In Education
Solve quadratic equations
Find roots of polynomials
Simplify complex fractions
Graph functions accurately
Prepare for calculus
In Technology
RSA encryption for online security
Password protection systems
Blockchain validation
Digital signatures
Error detection in data
In Professional Fields
Engineering calculations
Financial modeling
Data compression
Signal processing
Algorithm optimization
Every time you shop online securely, factoring protects your credit card. Every encrypted message uses prime factorization. The math you learn today builds the technology you use tomorrow.
Why Use Our Factoring Calculator?
Feature | Our Calculator | Other Calculators |
|---|---|---|
Speed | Under 1 second | 2 to 5 seconds |
Step Shown | Always included | Sometimes missing |
Mobile Friendly | Perfect on all devices | Often buggy |
Cost | Free Forever | Often requires payments |
Accuracy | 100% verified | Varies by site |
Common Factoring Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake 1: Forgetting to Check for GCF First
Wrong: Factor x² + 5x + 6 from 2x² + 10x + 12
Right: Pull out 2 first → 2(x² + 5x + 6) → 2(x + 2)(x + 3)
Mistake 2: Wrong Signs in Trinomials
Wrong: x² – 7x + 12 = (x + 3)(x + 4)
Right: x² – 7x + 12 = (x – 3)(x – 4)
Remember: When b is negative and c is positive, both factors are negative!
Mistake 3: Not Verifying Your Answer
Wrong: Write answer and move on
Right: Multiply factors back to check: (x + 2)(x + 3) = x² + 5x + 6 ✓
Mistake 4: Mixing Up Sum vs. Difference of Cubes
Wrong: Using the wrong formula
Right:
- Sum: a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a² – ab + b²) ← minus in middle
- Difference: a³ – b³ = (a – b)(a² + ab + b²) ← plus in middle
Mistake 5: Trying to Factor Prime Expressions
Wrong: Spending 10 minutes on x² + 5x + 3
Right: Check all factor pairs quickly. If none work, it’s prime!
Benefits of Using an
Online
Factoring Calculator
Using an online factoring calculator makes the whole process faster, clearer, and far more accurate than doing it by hand.
It instantly handles everything from simple numbers to complex algebraic expressions, making it a reliable tool for students who want to double-check their homework and avoid manual mistakes.
Teachers save time by using it to verify solutions, while analysts, coders, and engineers appreciate the step-by-step breakdowns that help them validate their calculations.
Since it works smoothly on any device, it’s always accessible whenever you need quick, correct factorization without the frustration of manual work.
Important Factoring Terms
Know these terms to understand factoring better.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore More Factoring Tools
Check out these specialized calculators for specific types of factoring problems
Prime Factorization
Calculator
Break any number into its prime factors
Trinomial Factoring
Calculator
Factor polynomials with three terms
Difference of Squares
Calculator
Solve a² – b² patterns instantly
GCF
Calculator
Find the greatest common factor
Sum of Cubes
Calculator
Factor a³ + b³ expressions quickly
Difference of Cubes
Calculator
Factor a³ – b³ expressions quickly
Perfect Square
Calculator
Identify and factor perfect squares
Quadratic Factoring
Calculator
Factor quadratic equations
Start Factoring Now!
Ready to factor expressions instantly? Use our free calculator at the top of this page or try one of the quick examples.
No signup required. Works on any device. Get your answer in seconds.
Still have questions? Check our FAQ section above or explore our learning resources
